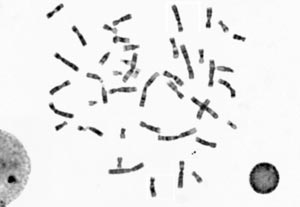
Chromosome classification
Chromosomes are organized structures containing most of living organisms’ DNA. Though important to detect major troubles to an individual’s growth, development and body functioning, the test which identifies and evaluates size, shape and number of chromosomes in the body cells needs human expertise, which is currently very rare. RSIP Vision decided to use convolutional neural networks to perform this chromosomes automated classification with machine learning.
Read More
Trajectory tracking of a fluorescent tag
Studying the behavior of bio-molecules and the interaction they have with other molecular structures in their native environment, developing indirect measuring procedures based on tracking of single particle, provides valuable information about processes like viral infections of cells, protein-DNA interactions and other complex biological processes. Analysis of trajectories of a tagged particle is one of many RSIP Vision’s projects tracking objects in a sequence of images with dynamic programming, one of our fields of expertise.
Read More
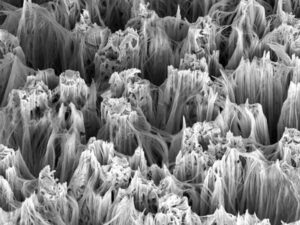
Reconstruction of rough surfaces with shape from focus
Reconstruction of the 3D shape of a surface viewed under the microscope is particularly challenging, owing to the irregular shapes that a surface can take. Irregular surfaces having many sharp bends and peaks have a high frequency texture pattern which needs to be smoothed out through a low-pass filter. The shape-from-focus method provides the framework to do just that, thanks to its ability to stably reconstruct a high frequency surface, as seen in electron microscopy.
Read More
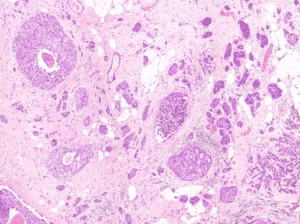
Detecting Mitosis Using Deep Neural Networks
State and progression of breast cancer are assessed through prognostic factors, one of which is the mitotic figure. In a histological sample taken from patients, the fraction of breast tissue cells undergoing replication is used to grade the cancer. RSIP Vision’s algorithms allow fast detection, recognition and classification of the mitotic state of a cell using automatic computational autonomous tools: deep neural networks help distinguish complex patterns in images and finally differentiate between mitotic and non-mitotic cells.
Read More
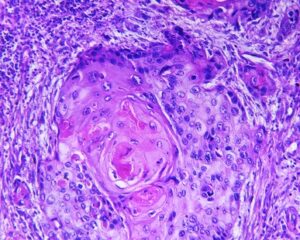
Automatic segmentation of tumor cells
Molecular analysis of in histology enables quantification of abnormality in a given tissue, assess patient condition, and devise treatment. Tissue samples taken in biopsy allow researchers to screen for therapeutic agents but might not accurately capture the bulk tumor, due to its irregular non-cylindrical shape. This calls for an automated segmentation of tumor cells: RSIP Vision does that in several phases, concluded by machine learning methods which study the cell texture and classify the image accordingly. The end result is a fast and life-saving biopsy scanning and analysis system.
Read More
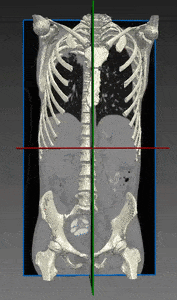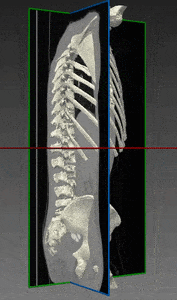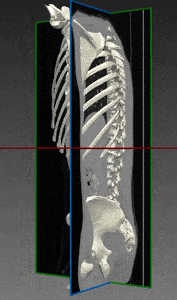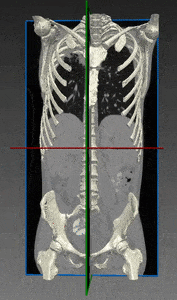
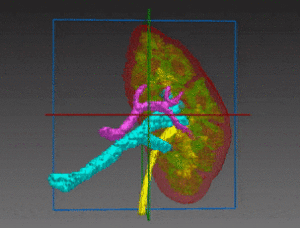
Bones and Skeleton segmentation
RSIP Vision suggests an automatic segmentation procedure based on iterative binarization of bone tissues density, as observed in Computed Tomography (CT), the most common 3D process used for bone imaging. This method is particularly fast, regardless of whether contrast was used in the CT scans. In fact, images taken with contrast generally display blood with an intensity which is similar to bone; our technique is able to overcome this challenge and to deliver a fast and satisfying bones segmentation and skeleton segmentation solution to our client.
Read More
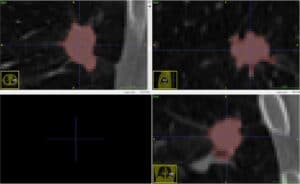
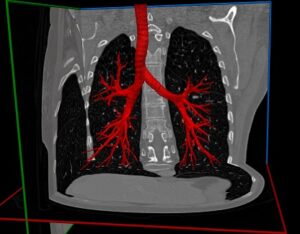
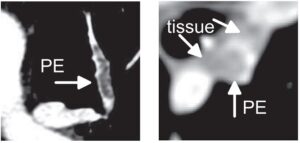
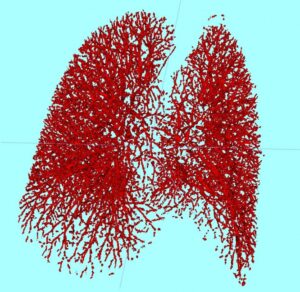
Lungs tumors and nodules segmentation with Deep Learning
It is visually more difficult to identify lung tumors than nodules, since the latter are supposed to have an elliptical shape, while the chromatic aspect of the former is quite hard to distinguish from healthy tissues on a CT image. We use Deep Learning neural networks to overcome this difficulty in a way that is quick to perform, reliable and memory efficient. Our software of computer vision in pulmonology detects and classifies tumors and nodules in the fastest time, to provide our clients a quick and reliable 3D segmentation of lung tumors with Deep Learning.
Read More
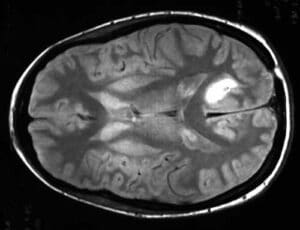
Brain tumor segmentation
In addition to primary tumors, the human brain can also suffer from secondary tumors or brain metastases. The most common cancers that spread from remote areas to the brain are lung, breast, melanoma, kidney, nasal cavity and colon cancers. By the way of segmenting the tumor in the image, brain tumor image processing overcomes anatomical structure challenges. AI-based techniques enable to estimate the volume and spread of the tumor and provide objective and variation-free expected tumor boundaries.
Read More
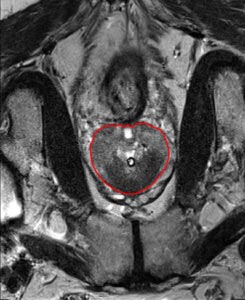
Prostate segmentation in MR images
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among American men, with more than 200,000 new cases diagnosed every year and about 1 man in 7 diagnosed during his lifetime. Volume is a key indicator of the health of the prostate, revealing key information about the stage of the cancer, the probable prognosis and viable treatment. The rich experience of RSIP Vision enables us to recommend an approach based on a semi-automatic prostate segmentation to give a precise estimate of the prostate volume.
Read More
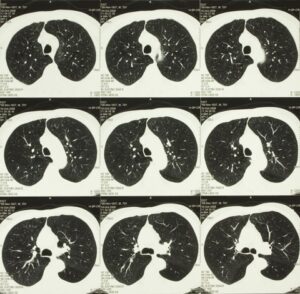
Lung Nodule Classification
Lung cancer early detection is a vital task which is made difficult by the small size of pulmonary nodules, the detection of which on thousands of CT scans every day is excessively time-consuming. Computer-aided lung nodule classification can dramatically boost the speed of diagnosis. Recommended solution starts from bidimensional images obtained from CT scan and displaying suspicious nodules areas: these are inserted into an autoencoder, from which two hundred dimensional features are extracted. These learned features are then confronted with a trained classifier to produce the final lung nodules classification.
Read More