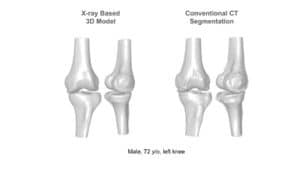
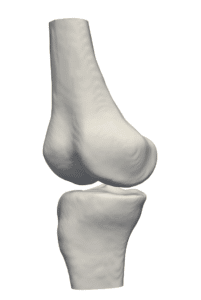
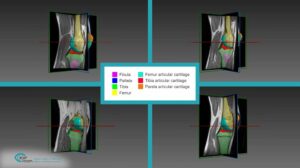
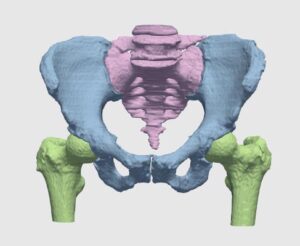
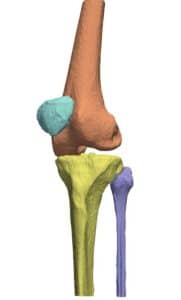
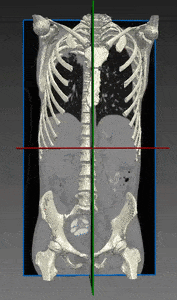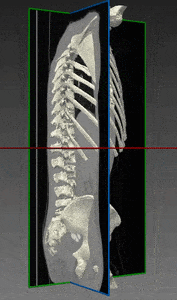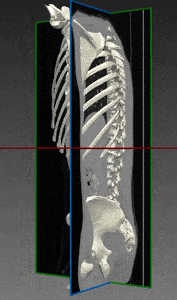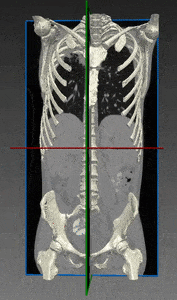
Computed tomography (CT) is the most common 3D process used for bone imaging. This is due to the fact that simple thresholding is usually sufficient to identify the bone tissue, based on its higher attenuation of X-rays as compared to soft tissues. The representation of a tridimensional model out of the many bidimensional CT slices has become a valuable and necessary process in many medical applications, enabling 3D observation of fractured bones and registration of other images using bones and skeleton as a region of interest.
However, only cortical bone offers the favorable high density needed to differentiate it from soft tissues. A large proportion of the human skeleton is made of porous spongy bone, which provides structural support and flexibility without the weight of compact bone. This spongy (or cancellous) bone offers only low X-ray attenuation, resulting in data density equal to or only slightly higher than that of soft tissues. This is even truer among elderly patients, who are the population most suffering from bones weaknesses and diseases.
The actual intensity scale used in CT as a measurement to assess bone density is the Housfield unit (HU): by definition, air has a value of -1000 HU and water has a value of 0 HU. Bones range from several hundreds to +3000 for dense bone.
Manual image editing and segmentation has long been used to extract bone geometry, but it is an extenuatingly long process with high inter-operator variability. Whatever the methods for segmenting CT images, a manual correction is usually called for in the bone contouring process.
The solution suggested by RSIP Vision utilizes state of the art deep learning models in combination with vast knowledge in computer vision to provide an algorithm that accurately segments bones in CT scans, with high speed and robustness to CT variations and artifacts.
To train this top notch AI, multiple scans were first annotated via our proprietary computer vision algorithm for initial bones segmentation, based on bone geometry, gradients and texture. After that, annotations are examined and further improved by our trained medical image analysts, working hand in hand with radiologists. With that, the optimal segmentation of bones and skeleton is achieved.
We have found this method particularly fast, regardless of whether contrast was used in the CT scans. In fact, images taken with contrast generally display blood with an intensity which is similar to bone; our technique is able to overcome this challenge and to deliver fast and satisfying bones segmentation and skeleton segmentation to our client.
The actual intensity scale used in CT as a measurement to assess bone density is the Housfield unit (HU): by definition, air has a value of -1000 HU and water has a value of 0 HU. Bones range from several hundreds to +3000 for dense bone.
Manual image editing and segmentation has long been used to extract bone geometry, but it is an extenuatingly long process with high inter-operator variability. Whatever the methods for segmenting CT images, a manual correction is usually called for in the bone contouring process.
The solution suggested by RSIP Vision utilizes state of the art deep learning models in combination with vast knowledge in computer vision to provide an algorithm that accurately segments bones in CT scans, with high speed and robustness to CT variations and artifacts.
To train this top notch AI, multiple scans were first annotated via our proprietary computer vision algorithm for initial bones segmentation, based on bone geometry, gradients and texture. After that, annotations are examined and further improved by our trained medical image analysts, working hand in hand with radiologists. With that, the optimal segmentation of bones and skeleton is achieved.
We have found this method particularly fast, regardless of whether contrast was used in the CT scans. In fact, images taken with contrast generally display blood with an intensity which is similar to bone; our technique is able to overcome this challenge and to deliver fast and satisfying bones segmentation and skeleton segmentation to our client.

 Orthopedics
Orthopedics