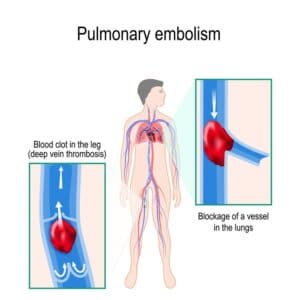
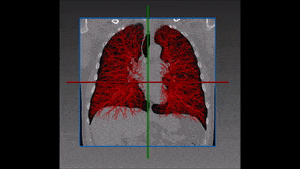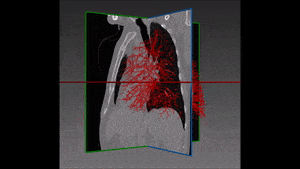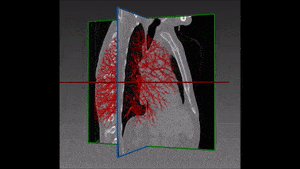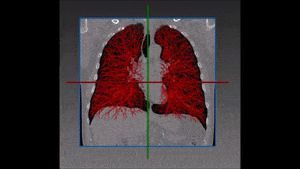
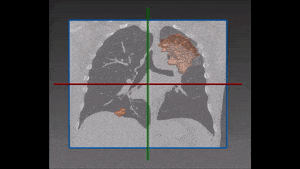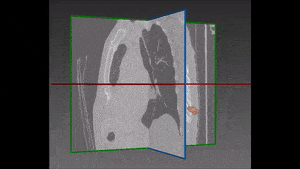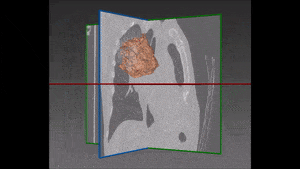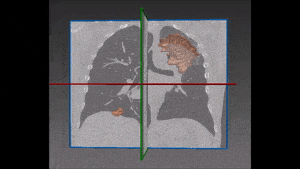
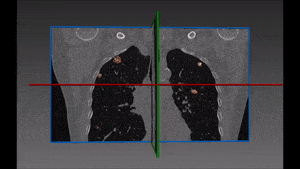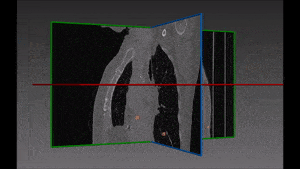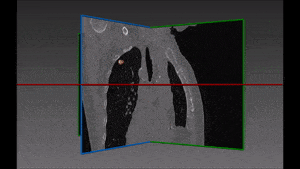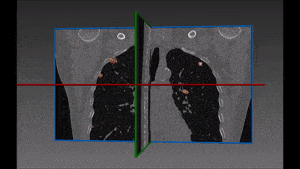
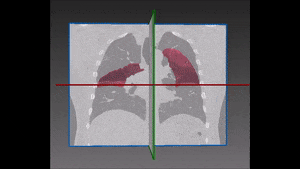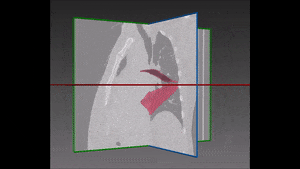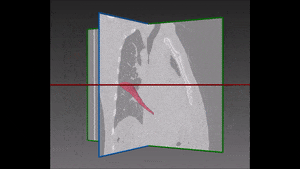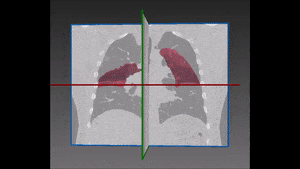
The left lung is divided in two lobes, the upper and the lower lobe. These two lobes are separated by an oblique fissure (the left major fissure). In the right lung, an oblique fissure (the right minor fissure) and a horizontal fissure (the right major fissure) separate the lung into three lobes – the upper, the middle, and the lower lobe. Each lobe has its own pleural covering. The two human lungs are thus divided in five lobes.
Lung lobes segmentation is particularly important during the process of assessing the location and progression of diseases, as well as when choosing their most appropriate treatment. Emphysema quantification and lung nodule detection are among the clinical applications which benefit the most from lung segmentation in CT scans. In fact, proper lung segmentation is key to determine the boundaries of lobes and prevent pleural damage during examination and treatment. When correctly located, diseases can be treated faster and better, hence the need to find a faster alternative to manual segmentation, which is time consuming and therefore far from ideal.
The main obstacle to lung segmentation comes from differences in anatomy and deformed or incomplete fissures: in fact, anatomical variations are the reason why atlas registration gives better results when performed on healthy and regular lungs. The results of atlas and multi-atlas approaches are less satisfactory when the lungs differ significantly from the atlas because of ailments, shape variations or simply an incomplete fissure on the CT scan.
Our client needed a solution to perform fast and reliable pulmonary lobes segmentations. Among the many approaches which have been recently tested by the scientific community, we achieve the best result by combining several techniques around a watershed transformation.
Our approach at RSIP Vision starts with a segmentation of the pulmonary vessels: this phase is particularly helpful since it is assumed that no major blood vessel is to be found in the proximity of the fissures. This first step enables to separate the pulmonary vasculature from other dense structures which are more suitable to be fissures candidates. This is done using information coming from vessels, fissures and bronchi while giving a fissure probability to each voxel by the way of a Hessian matrix fissure enhancement procedure.
The enhancement of the fissures which is implemented with this technique attributes to each voxel a fissure similarity value comprised between 0 and 1. These results are then converted to a segmentation of the lobe fissures, following criteria such as minimal similarity and range of intensity.
The following step of our solution is built on our own variation of a watershed transformation technique performed starting from an initially segmented fissure and successively extended to the surrounding region of interest. The information coming from vessels, fissures and bronchi is thus combined into a cost image which, together with 3D markers of the five lobes, is used as input of this watershed transformation.
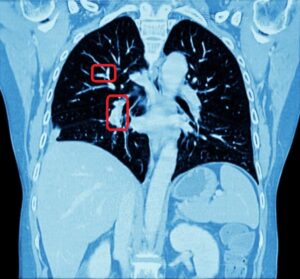
The robustness of this lobe segmentation has been successfully tested on a set of lungs showing incomplete fissures, since these are the most challenging cases in lung segmentation. The results of the comparison prove that a correct segmentation can show far better results than those which are immediately visible on a CT image.

 Pulmonology
Pulmonology