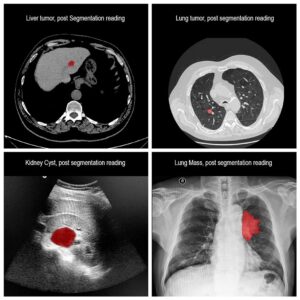
Molecular analysis of in histology is a powerful tool to explore prognostic markers after tissue staining. High throughput analysis of histological tissue enables quantification of abnormality in a given tissue, assess patient condition, and devise treatment. Tissue samples taken in biopsy allow researchers to screen for therapeutic agents by exposing the sample to a combination of drugs. Both expression levels and tissue morphological changes indicate response to a certain combination of drugs and can orient therapeutic avenue.
Manual segmentation of tumor cells:
Common practice in histological analysis is to have two or more experts score the tissue response pattern. This visual examination is highly time-consuming and not readily available in clinical applications, where rapid intervention is crucial. Even for research purposes, tissue sampled in biopsy might not accurately capture the bulk tumor due to its irregular non-cylindrical shape. Therefore, segmentation of tumor cells by humans is quite unpractical and estimating the tumor burden becomes a non-trivial task even to human experts.
Fast scanning and analysis of histological tissue can be achieved by employing computer vision algorithm. These algorithms can autonomously perform quantification tasks, like estimating subpopulation fraction. Alternatively, they can achieve a semi-automated segmentation of tumor cells, working cooperatively with the human expert.
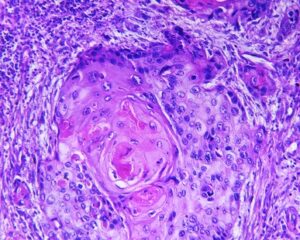
Automated tumor cells segmentation:
Quantification of biomarker expression in a cancer sample tissue is based on segmentation and classification of the image into several classes. At first, tissue stains need to be de-convolved to examine the expression distribution among cells belonging to the tissue under observation. The color histograms are basic tools allowing separation of the image into several independent color channel histograms, allowing grouping of pixels into classes.
Next, morphological analysis of the cells forms a second level of separation. Abnormalities in cells often are detected by nuclear shape abnormalities. Segmentation of nuclei can be performed on the image histogram by maximal entropy segmentation into several layers, each layer representing a band of entropic image intensity values. Subsequent processing of the entropic image intensity values result in binary segmentation into nuclei and non-nuclei pixels. To complete nuclei segmentation, morphological operations are used to reduce false detection.
Machine learning methods complement the tumor cells segmentation process by studying the cell texture and assign one of several predefined labels to pixels. The heterogeneous biopsy samples include regions of cancerous cells and others which are either normal like stroma, lymphoid, or inflammatory cells bordering and located within the tumor sub-population. The classifier training process can then study tissue features related to texture and classify the image accordingly.
The end result is a fast biopsy scanning and analysis system. Performing as an alert system for abnormality, this tumor cells segmentation system can save precious time and money. The learning systems allows incorporation of novel histological knowledge.
At RSIP Vision, we specialize in constructing learning systems and computer vision applications. Our company has a vast experience in microscopic images, whether in biology or in the chip industry applications.

 Medical segmentation
Medical segmentation