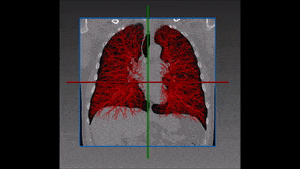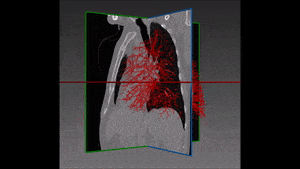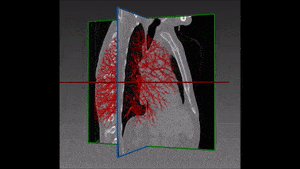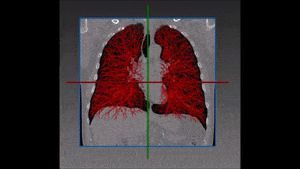
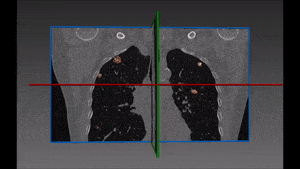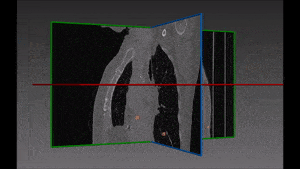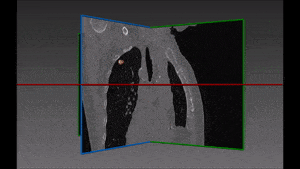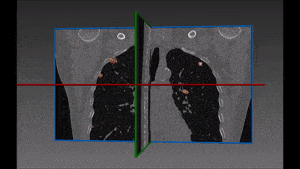
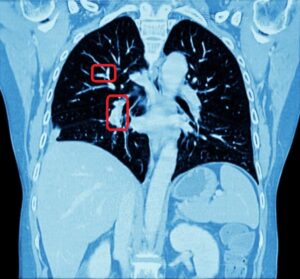
Lung cancer is the major cause of cancer death and the second most common cancer among men and women in the United States. It accounts for about 13% of all new cancers (more than 220,000 in the U.S. in 2015)*. Statistics on survival in people with lung cancer vary depending on the stage or extent of the cancer when it is diagnosed. Computer-aided diagnosis, aiming at performing a lung nodules classification to determine whether a nodule is malignant or benign, can assist the medical experts by making the detection process both faster and more precise, with massive life-saving consequences.
Lung cancer early detection is made difficult by the small size of pulmonary nodules, which cannot be detected by regular X-rays, and by the long time needed to classify the nodules seen on CT scans in thousands of new patients every day. Computer-aided lung nodule classification offers support to radiologists by providing automatic detection and analysis to speed and improve their manual observations.
Lung cancer early detection is made difficult by the small size of pulmonary nodules, which cannot be detected by regular X-rays, and by the long time needed to classify the nodules seen on CT scans in thousands of new patients every day. Computer-aided lung nodule classification offers support to radiologists by providing automatic detection and analysis to speed and improve their manual observations.
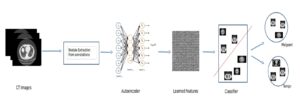
The use of deep learning can significantly boost the performance of computer-aided diagnosis systems. We recommend the use of a deep learning features extracted from an autoencoder: autoencoders are simple learning circuits, the purpose of which is to transform inputs into outputs with the least possible amount of distortion. Though their notion is relatively simple, they play a key role in the design of machine learning processes.
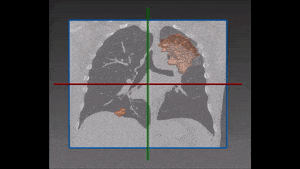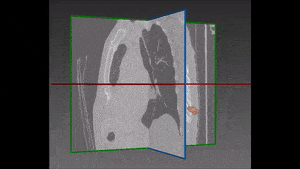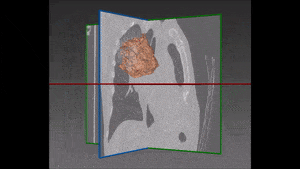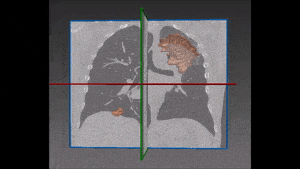
Our recommended solution starts from a bidimensional image obtained from CT scan and displaying suspicious nodules areas, as selected by the radiologist with the support given by previous biopsy, surgical inspections and other clinical sources of information. These areas are then inserted into the autoencoder and learned features are successively extracted. Following that, these features are confronted with a trained classifier to produce the lung nodules classification we are aiming at. For each nodule, two hundred dimensional features (obtained from the autoencoder) are given as input to the decision tree.
Accuracy of results is very high, though it depends on the visual similarities of nodules: the more dissimilar they are, the more reliable the lung nodule classification will be. This will also enable to keep false positives at a very low level, though of course the main concern of the study is to avoid false negatives, which would prevent the timely treatment of the disease with potentially fatal consequences. In this area, the system compellingly outperforms traditional methods. Its main breakthrough is that deep learning features also take into account the association between the different morphologic findings in the lung like presence or absence of lobulation, coarse spiculation and so on.
A very promising future direction of the research will require to integrate in the system an automatic detection of nodules with no previous use of human involvement such as radiologist-constructed lung nodule outlines.
* Source: cancer.org
Accuracy of results is very high, though it depends on the visual similarities of nodules: the more dissimilar they are, the more reliable the lung nodule classification will be. This will also enable to keep false positives at a very low level, though of course the main concern of the study is to avoid false negatives, which would prevent the timely treatment of the disease with potentially fatal consequences. In this area, the system compellingly outperforms traditional methods. Its main breakthrough is that deep learning features also take into account the association between the different morphologic findings in the lung like presence or absence of lobulation, coarse spiculation and so on.
A very promising future direction of the research will require to integrate in the system an automatic detection of nodules with no previous use of human involvement such as radiologist-constructed lung nodule outlines.
* Source: cancer.org

 Pulmonology
Pulmonology