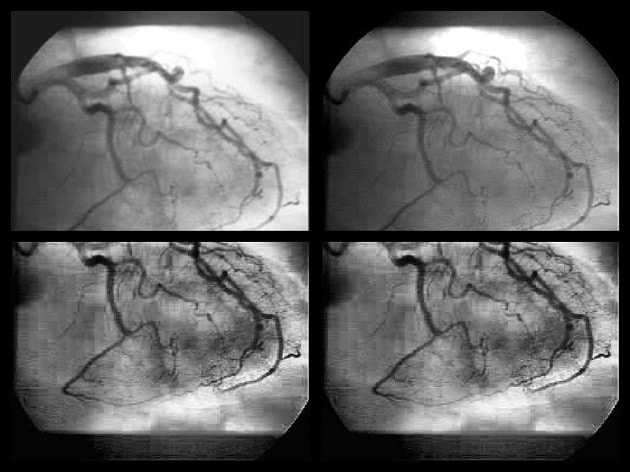
3D reconstruction of the heart
Using minimal 2D images from a routine angiography, RSIP Vision’s algorithm tracks the veins and constructs a route map of the arteries, from two different angles. Our sophisticated algorithms applied to computer vision in cardiology reconstruct 3D models of the heart artery tree from 2D images, allowing for improved diagnostic capabilities, lower risk to both patients and physicians, more effective therapy and reduced costs.
Read More
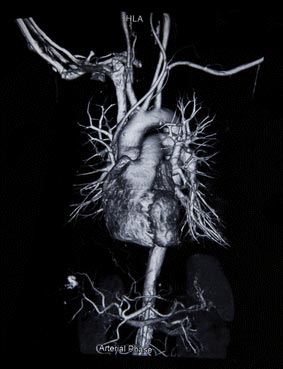
Coronary CT Angiography with Deep Learning
The production of 3D CT images of the heart requires a fast image processing technology, applied simultaneously on multiple scanned layers. To automatically separate the different components of the image, our software locates in the images the muscular layer (myocardium) of the heart needed for the rest of the segmentation in coronary CT angiography. Minimum graph cuts is the technique which provides the clearest tracking and the strongest segmentation results.
Read More
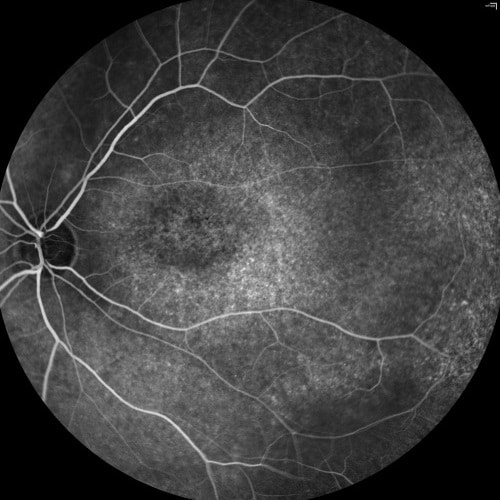
Stabilization in fluorescein angiography
One of the most common tests in ophthalmology is fluorescein angiography: fluorescein is injected in the blood and it moves immediately through the blood vessels
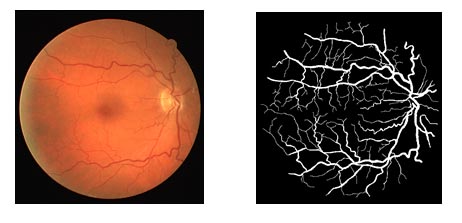
Vessel Segmentation Using Deep Learning
Various segmentation methods, whether based on Convolution Neural Networks or traditional image processing techniques, can be used to delineate the vascular tree in clinical imaging. Given the few features distinguishing veins from arteries (usually brighter and thinner than veins), the challenge consists of training a binary classifier assigning each pixel to the category of vein or artery. This article covers the advantages of using CNNs and deep neural networks for the classification and segmentation of vessels in fundus images.
Read More
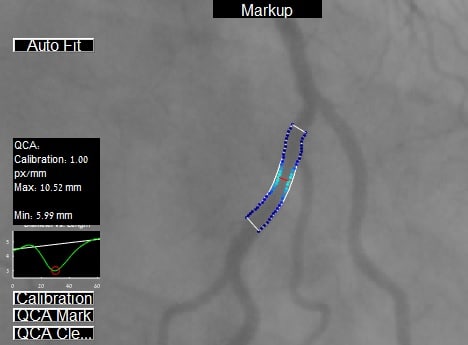
Quantitative Coronary Analysis
The main contribution of Quantitative Coronary Analysis (QCA) consists in measuring the diameter of arteries. Angiograms provide coronary images of region suspected of lesions using which our advanced algorithms for vessel detection and segmentation measure the segmented artery’s diameter. Abnormal values (as compared to a constructed reference diameter) are suspected as stenosis. Our system extracts and displays relevant values to the view of medical professionals and their patients.
Read More
