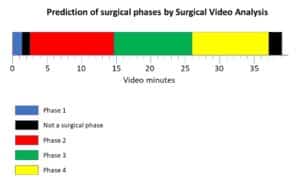
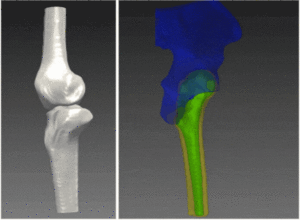
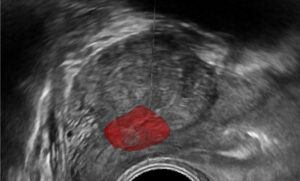
The objectives of this validation are two:
- First, to ensure that the tracking system’s accuracy complies with FDA standards.
- Second, to maintain this level of accuracy during the system life cycle.
Validation of Accuracy – Procedure
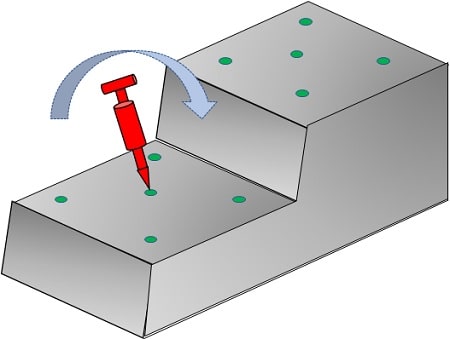
Validation of accuracy is performed using a standard (ASTM) jig. This jig contains a set of locations with their X, Y and Z values. In addition, the jig contains a marker, whose function is to log the jig’s location in the world. During the testing process, the surgery tool is moved between the jig points at some standard sequence. It is parked at each jig point for a short duration, though long enough to let the system record its location. The ASTM software calculates the X, Y Z location relative to the first (“world”) location. Each coordinate is then validated to be within the ASTM tolerance from the corresponding reference point.
Additional testing checks the location accuracy in cases where the tool is held diagonal to the jig’s surface at a few reference angles. This test ensures that accuracy is maintained for various working orientations.
This is the fifth and last in a series of five articles about Orthopedic Navigation. Keep reading about RSIP Vision’s work in image processing for Orthopedic Surgery. Do you want to talk to our engineers about your project in orthopedics image processing? Contact them here!