MLOps for AI in Medical Imaging
The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for medical imaging is a complex task, with unique challenges and stringent regulatory requirements. In particular, the development process of the model should be transparent and traceable, with a clear understanding of why a specific model and/or data configuration was selected. Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) provides a structured approach to address these challenges, ensuring that AI models transition from proof of concept (PoC) through FDA approval to clinical deployment as efficiently and robustly as possible.
Unlike regular DevOps which is geared to ensuring quality control with multiple developers working on the same project, MLOps is geared to enabling and ensuring a rigorous scientific approach to machine learning. This is achieved using controlled and fully documented “experiments”, with each experiment representing a different configuration of data, model and evaluation metrics. This post explores how we implement MLOps principles at RSIP Vision, exemplified through the ClearML platform.
The main principles of MLOps are:
Version Control for Everything: Not just code, but also data, models, configurations, and experiments.
Automated Experiment Tracking: Logging every detail of model training, from hyperparameters to performance metrics.
Reproducible Workflows: Ensuring that any experiment or deployment can be recreated identically.
Model Lineage and Governance: Understanding the full history of a model, from its training data to its final deployment.
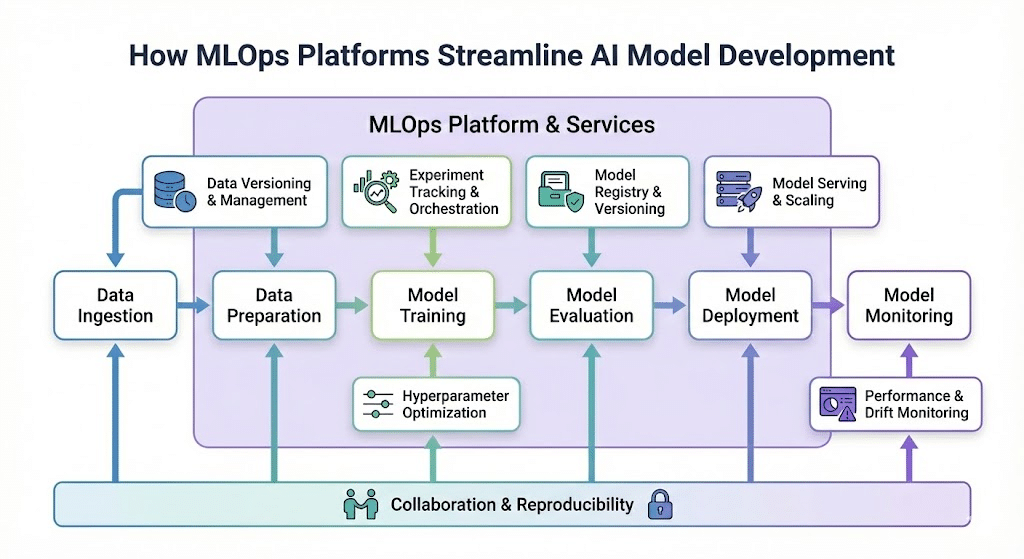
ClearML: A Technical Deep Dive into MLOps for Medical Imaging
ClearML is an open-source MLOps platform that offers comprehensive tools for experiment management, data versioning, model management, and MLOps automation. Its design makes it particularly well-suited for the demanding environment of medical imaging AI development.
1. Experiment Tracking and Reproducibility
ClearML’s Experiment Manager automatically logs every aspect of a training run when integrated with common ML frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras, scikit-learn). This ensures that each experiment is fully reproducible, thus facilitating regulatory audits and scientific verification.
Each time a training session is run with ClearML initialized, the following are recorded:
Code Snapshot: The exact Git commit, uncommitted changes, and dependencies (pip packages).
Hyperparameters: All argparse arguments, configuration dictionaries (e.g., loaded from YAML files), and manual parameter settings.
Metrics & Artifacts: Scalar metrics (e.g., Dice coefficient, accuracy, loss), confusion matrices, ROC curves, and visual artifacts (e.g., example segmentations, activation maps) are automatically captured.
GPU/CPU Usage: Resource consumption is tracked.
2. Data Versioning and Management (ClearML Data)
ClearML Data functions as a data version control system, which is especially relevant for medical datasets which require clinically relevant data and high quality annotations. This provides a verified link between a model and the data it was trained on, which is critical for FDA submissions. The framework allows developers to:
Version Datasets: Each modification to a dataset (e.g., adding more cases, correcting annotations) results in a new, immutable version.
Track Lineage: Every experiment explicitly links to the specific dataset version it used.
Manage Large Files: It intelligently handles large files, often storing them efficiently on remote storage (S3, GCP, Azure Blob) while keeping metadata in ClearML.
Access Control: Permissions can be set for who can access or use specific dataset versions.
3. Model Management and Registry
ClearML’s Model Gateway (Model Registry) allows models (artifacts) logged from experiments to be explicitly registered, tagged, and versioned. This allows full tracking between models undergoing various stages of the development process (QA, clinical validation, deployment), and the experiments used to create the models. The platform provides:
Centralized Repository: All trained models are stored in a searchable registry.
Metadata Rich: Each model links back to its originating experiment, including all training logs, hyperparameters, and dataset versions.
Versioning: Models can be explicitly versioned.
Approval Workflows: Implement staged approvals (e.g., “Development”, “QA”, “Production”) for models, essential for medical device certification.
Conclusion
MLOps, and platforms like ClearML, are not merely organizational tools; they are technical necessities for developing robust, compliant, and deployable AI solutions in medical imaging. ClearML addresses this challenge by providing granular experiment tracking, immutable data versioning, structured model management, and comprehensive automation capabilities.
MLOps empowers the algorithm team at RSIP Vision to concentrate on providing value for our customers rapidly and with minimal resources. On the other hand, it ensures that even a PoC has a solid foundation from which to migrate to a fully FDA approved product, and from there to clinical deployment.