Prostate Cancer and PI-RADS scoring
Prostate cancer is the most common male cancer in the USA. When diagnosed early, mortality rates are very low, therefore, most men over the age of 60 years undergo screening for prostate cancer that includes PSA levels and digital rectal examination. Common practice dictates that when Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels are high, or when the patient is in a higher risk group, a prostate MRI scan is performed. This scan is read by a radiologist in search of lesions.
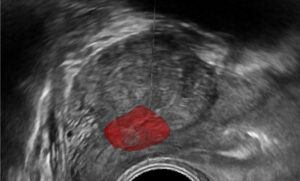
To set an objective diagnosis for prostate lesions in MRI, the PI-RADS (Prostate Imaging–Reporting and Data System) score was developed. It accounts for the lesions’ intensity, restriction, size, and shape, and provides a standardized score for reporting among physicians. Whenever a prostate MRI scan is conducted, the radiologist carefully examines it and determines a PI-RADS score for the patient. This process is highly subjective and time-consuming.
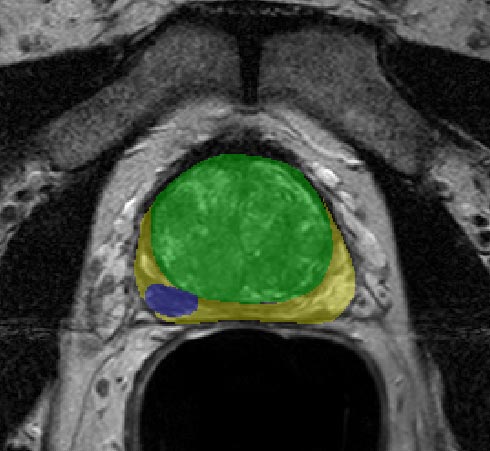
PI-RADS scoring
The score ranges from 1 to 5. In PI-RADS scores 1 and 2, no further follow-up is needed unless there is a change in the clinical examination or the PSA levels. PI-RADS 3 is equivocal, for some lesions the radiologist will recommend either follow-up or biopsy. PI-RADS 4 and 5 mandate biopsy as they infer a high risk of cancer.
When follow-up is recommended, it is termed active surveillance or watchful waiting – continuous imaging and biopsies, depending on the medical recommendation. When the followed-up lesion develops into carcinoma, the surveillance is discontinued, and the urologist actively treats the cancer (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or combination therapy). In patients who are high-risk for surgery (old, debilitated, serious background diseases, etc.), even a PI-RADS score of 4-5 may lead to continuous follow-up.
In active surveillance/watchful waiting, a prostate MRI scan is performed and compared to previous scans. Any dynamic change (positive or negative) in the lesion characteristics needs to be documented and measured, as it may be the trigger to stop active surveillance and proceed to active treatment. This leads to high volumes of prostate scans which need to be analyzed by radiologists – quickly and accurately.
Artificial Intelligence in prostate MRI
Currently, the precision of the radiological follow-up is highly dependent on the physician’s experience and the scan conditions. One of the best ways to ensure objectiveness is by implementing AI and deep learning into the practice.
AI and computer vision algorithms are capable of segmenting, detecting, and comparing structural and visual changes in the prostate, specifically the volume, intensity and restriction of the lesions. These changes can be recorded and presented to the radiologist for review prior to diagnosis, providing robust tools for an accurate comparison.
Other Similar Use-Cases
Women at risk of breast cancer (BRCA carriers, family history) often undergo annual breast-MRI exams as a surveillance tool. Similar to prostate cancer, these scans can be automatically assessed and compared, providing an accurate map for differences between scans. By applying the same technology of the PI-RADS assistant to breast MRI, we can get a BI-RADS assistant.
RSIP Vision’s Solutions
RSIP Vision has a long, proven track record of AI and deep-learning solutions for multiple medical devices. Our team of clinicians and engineers can tailor a solution for PI-RADS scoring assistance for any device or platform. Contact us today to speed your device production and time-to-market!

 Urology
Urology