Every deep learning based system requires sufficient data for proper training and reliable testing. Therefore, data collection and annotation are the first and foremost required processes when approaching a deep-learning solution. Medical data, specifically videos from robotic assisted surgeries (RAS), present several challenges in this aspect:
- Availability – There is a limited number of surgeries performed. One cannot conduct specific surgeries or request for a surgery to be conducted in a specific manner for the purpose of data collection.
- Privacy – Medical data in general, and robotic data specifically, contains information which cannot be shared publicly, such as private patient info, and anonymization and verification of this info is mandatory.
- Ownership – It is often unclear to whom the data belongs (hospitals, patients, healthcare systems). Permission to use it is crucial, but can be tricky to obtain.
- Labeling – Manual annotation of data is time consuming, and in most cases, it will require an expert (surgeon) to annotate.
- Legal – future lawsuits can be supported by medical data, and the medical team involved may refuse to share it unless they are certain the risk of lawsuit is negligible.
- Anatomy variability – There are major differences between anatomies, and it is challenging to have access to a wide variability of anatomical structures.
Generating RAS data
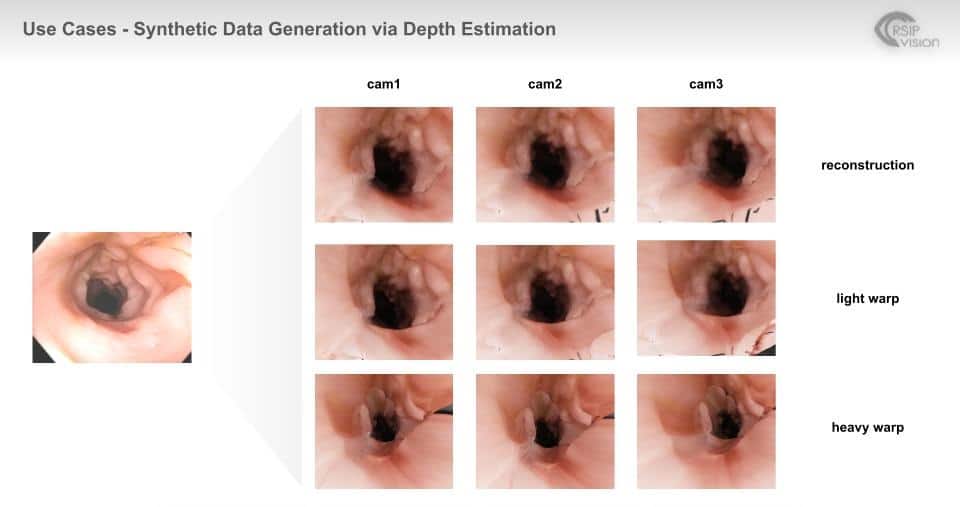
A solution to the above-mentioned challenges is to generate data synthetically. Synthetic data generation can be achieved using:
- Deep Learning – there are 2 main techniques in deep learning: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational AutoEncoders (VAEs).
– GANs are trained to take a random input and transform it to an image similar to the real data based on conditions previously determined.
– VAEs compress the real data input and decompress it to a similar image. - 3D Rendering – A 3D model of the scene is created and the color, lighting, camera point of view, etc. are selected. Here the annotation is done automatically by the 3D renderer.
Both methods can be applied to RAS scenes. GANs and VAEs have been widely used in many technologies (e.g. facial recognition, autonomous driving, etc.) and have proven successful in most. 3D rendering requires development of dedicated software which mimics the procedures desired and re-creates scenes from these procedures.
Advantages and applications of Synthetic Data Generation in RAS
Any application of Artificial Intelligence in RAS, specifically machine learning, requires training and testing sets. As described above, this data is complicated to obtain, especially edge cases. Generating data for network training can significantly improve performance by exposing the network to a larger variety of cases, while reducing annotation time. These networks, although trained on both real and synthetic data, can provide accurate segmentation, automatic recognition of objects, and applications for augmented reality (AR).
Another important use for generated data is surgeon training. Every surgical case is different, and acquiring proper surgical skills requires learning a variety of cases. This task is time consuming as not all cases are common. Creating a virtual reality (VR) training environment provides real training experience without the patient. Using synthetic data, a procedure can be custom-tailored to verify proper training for every surgeon.
Use Synthetic Data in your Device
Whether your output is synthetic surgical data or Artificial Intelligence modules for RAS, you can benefit from an expansive dataset with a variety of cases. RSIP Vision has a talented team of clinicians and engineers, verifying that the resulting synthetic data is relevant and accurate. Contact us today!

 Surgical
Surgical