GMS: Grid-based Motion Statistics
Every month, Computer Vision News reviews a research from our field. This
month we have chosen to review two papers. The first one is
GMS: Grid-based
Motion Statistics for Fast, Ultra-robust Feature Correspondence
. a
paperoffering a simple means to incorporate motionsmoothness in a way that
rapidly and reliablydifferentiates true and false matches in a region. Weare
indebted to the authors (
JiaWang Bian
and
Wen-Yan Lin
- as joint first authors -
as well as
Yasuyuki Matsushita
,
Sai-Kit Yeung
,
Tan-DatNguyen
and
Ming-Ming
Cheng
) for allowing us to use their images to illustrate this review. The website
of the project is
here .Background, motivation and novelty:
The main advantage of encapsulating smoothness constraints into feature
matching is the ultra-robustness of the generated results. However, the price to
pay is not negligible, in terms of complexity and slowness, which prevent the use
of such a technique for video. The challenge is to develop accurate and robust
matching of features between images, quickly enough and with computational
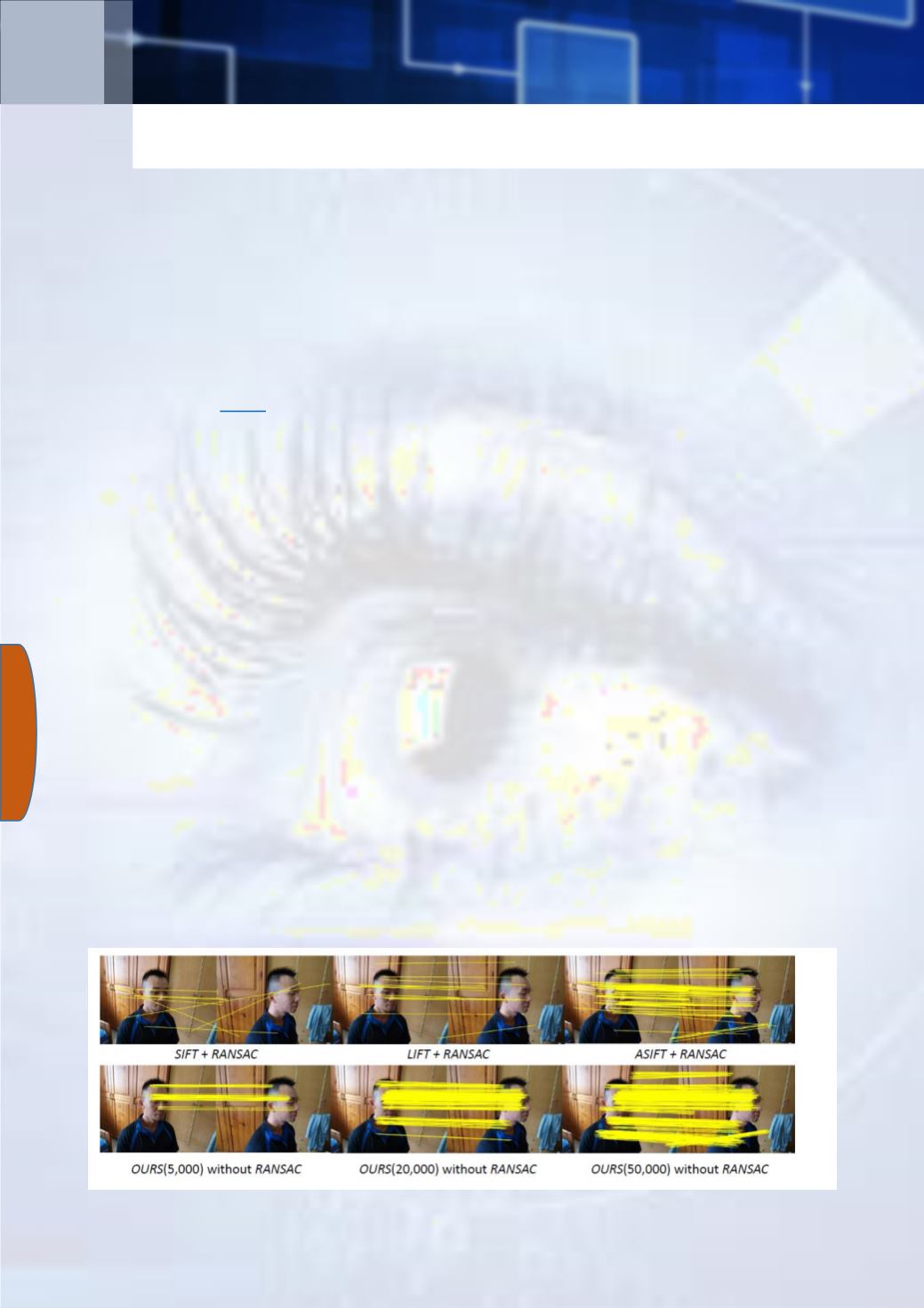
efficiency sufficient for real-time application. GMS, that is Grid-based Motion
Statistics, is the solution proposed by this paper to incorporate motion
smoothness as a statistical likelihood of having a certain number of feature
matches between a region pair by the way of differentiating true and false
matches - by evaluating the number of matches in selected neighborhood. The
assumption (largely inherited from previous works) behind this idea is that
motion smoothness induces correspondence clusters that are unlikely to occur
at random. Statistical measures (building on the law-of-large-numbers) are so
introduced to reject false matches and allow previously unthought-of results.
“GMS achieved real-time matching of features in challenging
scenarios, not yet successfully dealt with before”
48
Computer Vision NewsResearch
Research