During minimally invasive surgeries, surgeons are limited in their field of view, which restricts their observation of the patient’s full anatomy. This may lead to suboptimal surgical outcomes or even errors. For example, in a tumor excision procedure, healthy tissue may be injured, or worse, the surgeon may fail to optimally remove the lesion.
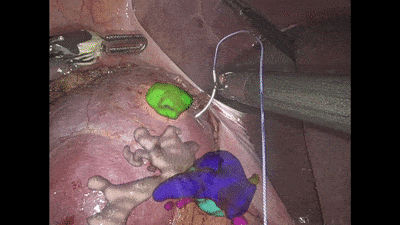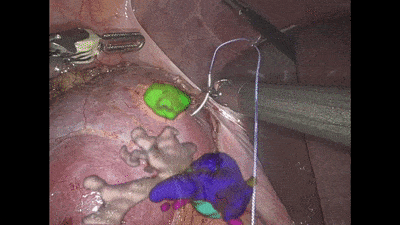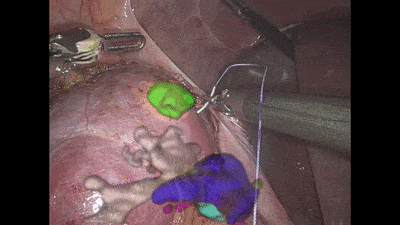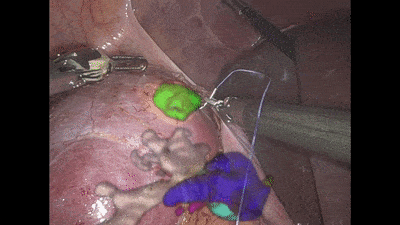
Surgeons base the procedure on pre-op images of the area such as CT scans, which provide a snapshot of the internal tissue. Navigation systems are then utilized to fit the scan to the coordinate system of the operating theatre, to inform the surgeon of the patient’s anatomy. However, all existing navigation systems are limited in their accuracy as tissues may be displaced during surgery, which distorts the mapping of the tissue to the pre-op scan.
The existing solutions are primarily useful in orthopedic scenarios, for example, insertion of a tracking pin into the spine or other bones or joints that provides a reference point for the moving bones. However, insertion of the tracking pin may be painful to patients, as well as causing trauma to the site of implantation and posing an inflammatory risk. Furthermore, it does not provide a solution for soft tissue movement during surgery. Soft tissues are easily displaced during surgery and cannot be fitted with a tracking pin, making it close to impossible to locate them accurately.
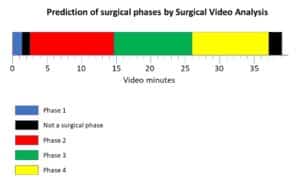
Soft tissue navigation is extremely important to improve brain, spine and kidney surgeries amongst others, as well as laparoscopy procedures. Advances in camera resolution, image processing techniques and artificial intelligence can vastly improve tissue tracking during surgery. AI algorithms may be applied to track and predict tissue distortion, which will enable the surgeon to better perceive the internal environment, increasing surgical accuracy and minimizing the risk of damaging healthy tissue. To achieve this, AI algorithms can be trained on appropriate medical data sets to track movement, leading to this predictive ability. We at RSIP Vision are applying this advanced technology to provide sophisticated surgical solutions.
Intra-op registration to pre-op scans of the anatomy is fundamental for visualizing soft tissue deformation and tissue displacement during surgery. Deep learning algorithms may be used to learn how tissues deform, to inform and improve registration. They allow large amounts of data to be leveraged, making them superior to previously developed hand-crafted algorithms.
At RSIP Vision we are actively developing these important and exciting technological innovations that will transform the face of intra-op navigation, making surgeries safer and more effective. So, if you want high-quality AI solutions for intra-op soft tissue navigation, contact us to book a call with our best specialists in Artificial Intelligence for surgery.

 Surgical RSIP
Surgical RSIP